what to use on diesel truck to clean sulfur buildup
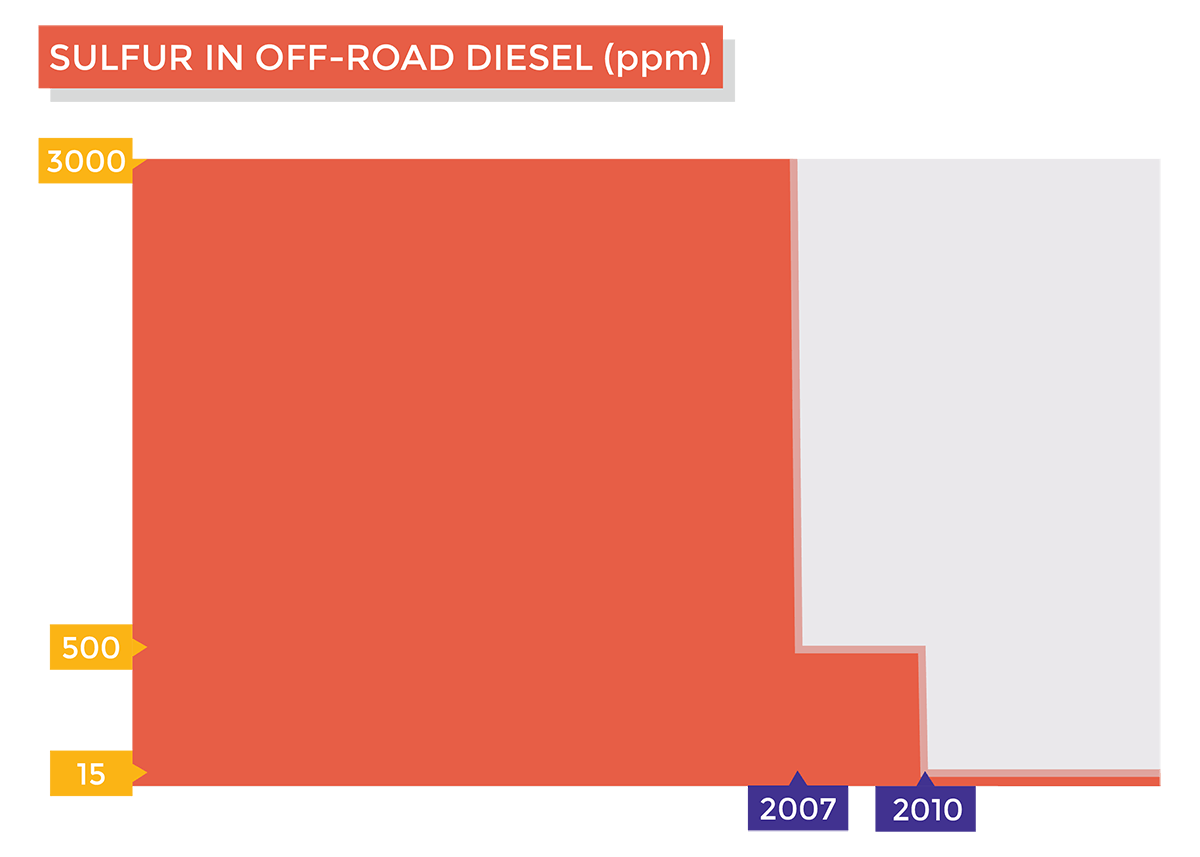
Yous accept probably heard mixed reviews virtually Ultra Depression Sulfur Diesel (ULSD). Some say it is bang-up for the environment while others merits information technology causes more than issues than information technology solves. If you are looking for an unbiased take on the ins and outs of ultra-depression sulfur diesel fuel, yous are in the right place. Below we cover why ultra-depression sulfur diesel fuel exists, its benefits and disadvantages vs. traditional diesel, and what you can practise to protect your vehicle or equipment from any negative side-furnishings of ULSD. In a nutshell, Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) was created in response to a number of regulatory actions aimed at reducing diesel fuel emissions. In 1970, Congress passed the Clean Air Act equally a ways to reduce harmful emissions from automobiles. The Clean Air Human activity was afterwards amended in 1990, requiring stricter emission reductions of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate affair. Concurrently, the EPA started imposing sulfur content limits on diesel in an effort to help buses and trucks become compliant with other emission standards coming into outcome that year. The master motivator for reducing overall emissions was to mitigate the harmful health and environmental effects caused past fossil fuel emissions. In 2001, the EPA finalized a federally mandated plan called the 2007 Heavy-Duty Highway Diesel fuel Plan. This plan was established to farther decrease emissions by enabling the use of advanced emission control technologies for new highway diesel fuel engines. Although effective, these technologies were establish to be easily damaged by sulfur, requiring serious sulfur reductions in diesel fuel in lodge for them to be used. Effective June 2006, the maximum sulfur limit in diesel was slashed from 500 to 15 parts per one thousand thousand (ppm). This reduction officially marked the switch from depression sulfur diesel fuel (500 ppm) to ultra-depression sulfur diesel (15 ppm). Soon after the highway diesel program'south inception, the EPA issued the Make clean Air Not-Road Diesel – Tier 4 Final Rule. This dominion mandated sulfur reductions for off-road diesel engines, constructive 2007. Every bit a event, the maximum sulfur limit in off-route diesel fuel dropped from 3,000 to 500 ppm in 2007 and later 500 to xv ppm in 2010. The intended event of lowering sulfur content in diesel fuel has led to many positives that tin be derived from the large reductions in harmful emissions. Unfortunately, to achieve reduced sulfur levels, the fuel must first exist processed. This processing has led to some less than desirable side furnishings due to the changes it makes to the fuel's chemistry. Whether the do good of reducing emissions outweighs the negative side furnishings of ultra-depression sulfur diesel fuel is a judgment nosotros will leave for y'all to brand. Since the 90s, EPA mandates have resulted in a 99.seven% reduction of sulfur content in diesel. This reduction is directly responsible for a decrease in sulfur dioxide (And then2) emissions which, lonely, have been a major correspondent to serious wellness and environmental bug. Health concerns related to sulfur dioxide (And then2) exposure include respiratory issues and lung damage. Tree, plant, and stone damage, acid rain, and brume are some of the ecology furnishings of sulfur dioxide (And thentwo) emissions. Sulfur reduction in diesel has also enabled the employ of avant-garde emission control devices in modern diesel engines. These devices have been able to reduce nitrogen oxide and particulate matter emissions past 90% and 95% respectively. Nitrogen oxide and particulate matter have both been institute to contribute to serious health problems such as premature mortality, aggravation of respiratory and cardiovascular affliction, aggravation of existing asthma, astute respiratory symptoms, chronic bronchitis, and decreased lung office. In addition to these issues, NOx and particulate matter emissions are suspected to exist carcinogenic and contribute to the development of lung cancer. In 2004, it was estimated that heavy-duty trucks and buses were responsible for about 1/3 of all nitrogen oxide and particulate matter emissions. By reducing emissions from these popular modes of transport, information technology can become apparently articulate that the benefits of ultra-low sulfur diesel lie in the betterment of both public health and the surrounding environment. Removing sulfur contents from diesel fuel has been shown to profoundly alter the lubricity and overall chemical composition of the fuel. Refineries employ severe hydrotreating to remove sulfur. This is a process that also happens to decrease diesel fuel's natural lubricity, lower free energy density (fuel economy), and increases overall production costs. While hydrotreating does increment the fuel's cetane level, well-nigh of the side effects of hydrotreating are less than desirable. The fuel economic system of ultra-low sulfur diesel is estimated to decrease by 1% and, according to the EPA, severe hydrotreating likewise increases fuel production costs past v to 7 cents per gallon. Even so, these costs may be significantly higher depending on the market, distribution, and other production factors. Lower fuel lubricity is known to contribute to increased engine wear which can too increase maintenance and repair costs for equipment that consume ultra-depression sulfur diesel. In 2007, pollution awareness and prevention were on the ascent as emission mandates came into full effect. Since so, tank corrosion has hit an all-fourth dimension high for both gasoline and diesel storage. A recent study suggests this may be symptomatic of fuel tankers participating in switch loading where tanker trucks might transport ethanol-based gasoline one day only to haul ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel the next. Alone, ultra-low sulfur diesel has a higher affinity to h2o than traditional diesel fuel. Water is known to be one of the principal contributors to tank corrosion while also fostering rapid microbial growth in diesel fuel. It has been shown that mixing ULSD with small amounts of biofuel, such as ethanol, may accelerate tank corrosion. This is due to the microbes in the diesel fuel digesting trace amounts of ethanol, creating high-plenty levels of acerb acrid to cause significant corrosion of the surrounding tank. In conclusion, the benefits of ultra-low sulfur diesel are undeniably noble but, every bit with many pregnant changes, there will always exist trade-offs to consider. Fortunately, there are a number of products and technologies created to help mitigate the undesirable side furnishings of ULSD. At that place may be several issues created from the processing of Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) only nigh none of them are unable to be addressed through the adoption of new fuel technologies and products. Every bit previously mentioned, hydrotreating diesel to remove sulfur does reduce overall lubricity and energy density (fuel economic system). To effectively address these issues, one can adopt a fuel additive, possibly addressing both issues with a single bottle. Using a fuel additive does require the individual to regularly dose their fuel supply upon fill-up, but the benefit they receive from doing may exceed that of but restoring what was lost during the hydrotreating process. Much similar the supplement industry, there is no shortage of fuel additive offerings on the market. Some of these options work quite finer while others are simply well-marketed "snake oil". When looking to adopt a fuel condiment we strongly encourage you practise your own enquiry before putting your difficult earn dollars to the test. AXI International provides a line of broad-spectrum fuel additives, all of which feature a broad set of benefits in improver to increasing fuel lubricity and improving fuel economic system. In many cases, it has been shown that our AFC fuel additives have more than paid for themselves with fuel efficiency gains alone. This is mainly achieved with a fuel catalyst which enables a more complete combustion of the fuel, burning more fuel for power in the engine and sending less unburnt fuel out the exhaust. To learn more about our fuel additives click here. If you would like to hash out our additive offerings with one of our experts, fill out the form here. Accelerated tank corrosion is no doubt a serious issue, particularly for companies storing large volumes of Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel (ULSD) for backup power applications. ULSD'south high affinity to h2o and the practice of fuel switching are two factors contributing to this alarming problem. Luckily, there is a solution to this in the form of regular fuel filtration. Water in diesel has long been an outcome leading to tank corrosion and rampant microbial growth ("the diesel bug"). When microbes proliferate in the fuel, they begin to produce a sludge byproduct that prematurely clogs onboard filters of connected equipment similar backup power generators. The clogging of these filters can lead to unplanned maintenance and downtime, a serious issue for mission-disquisitional facilities. In add-on to producing sludge, these microbes will break down trace amounts of biofuels, producing acetic acid. This acid, alongside water, contributes to accelerated tank corrosion. By regularly filtering water out of the fuel, one tin prevent accelerated tank corrosion from occurring. Without water, microbial contamination cannot occur, and without microbial contagion, acerb acid cannot be produced from the trace amounts of biofuel often constitute in ultra-low sulfur diesel. So 1 may enquire, how is it that h2o continually finds its way into the fuel and how practise I regularly filter h2o out of the fuel? To answer the first question, water is always present in fuel to some degree. This presence is usually higher in ultra-low sulfur diesel fuel and biofuels due to their chemistry. Through tank condensation, h2o is continually reintroduced into the fuel supply as warm days turn into cooler nights. To answer the second question, y'all mostly have two options to filter contaminants, such every bit water, out of your fuel supply: One tin can purchase a mobile fuel polishing cart or rent a service to bring specialized equipment to filter your fuel supply. This service is usually done in a reactive manner as regular fuel testing is carried out to observe if h2o or microbial contaminants have reached a certain level to justify the servicing. Although effective, this option is not recommended for mission-critical and fill-in ability applications due to its reactive nature. A lapse in fuel testing or filtration can easily lead to fuel contamination issues outside of tank corrosion such equally sludge and particulate aggregating. One tin also purchase and install a fuel maintenance system to automatically filter the attached fuel supply on a scheduled basis. This option requires minimal interest outside of periodic filter changes on the installed fuel filtration system. Regular fuel filtration is considered a best practice equally it ensures the fuel remains free of water and other damaging contaminants, protecting your tank and the attached equipment from the shortcomings of ultra low sulfur diesel and newer biofuels.Why Does Ultra Depression Sulfur Diesel fuel Exist?
Clean Air Act Amendment (1990):

Highway Diesel Plan (2001):
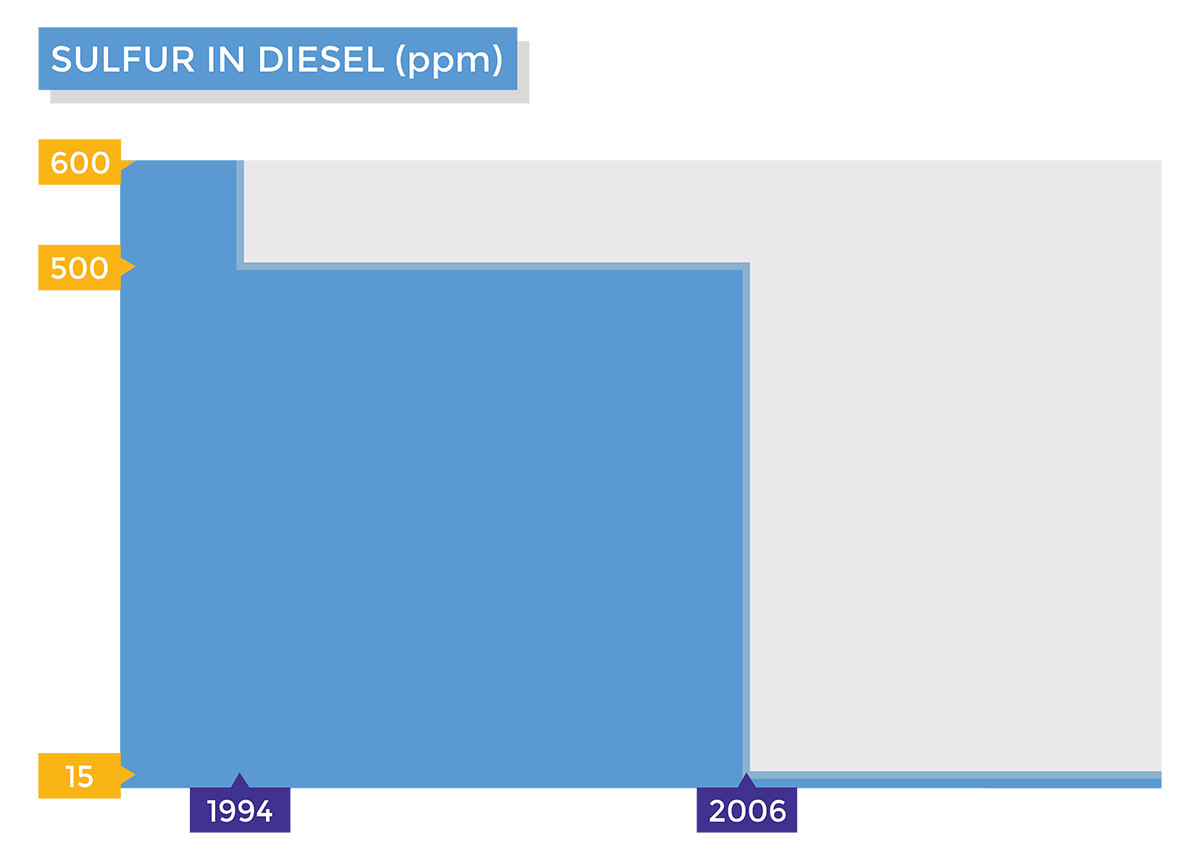
Clean Air Off-Road Diesel Rule (2004):
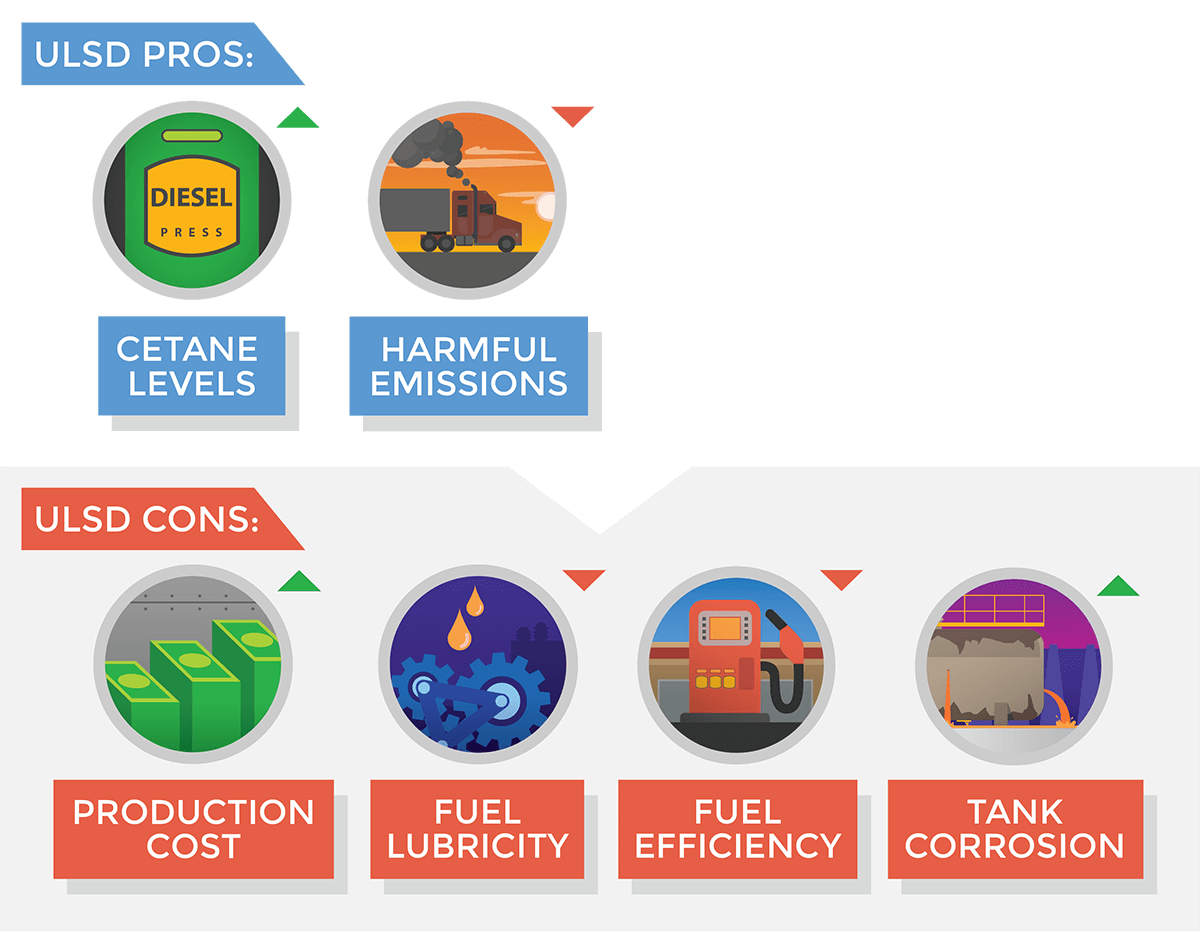
The Pros & Cons of Ultra Low Sulfur Diesel
The Expert: Emission Reductions

The Bad: Changes in Fuel Chemistry
The Rusty: Corrosive Effects of ULSD
Preventing Problems Acquired past ULSD
Addressing Reduced Lubricity & Fuel Economy
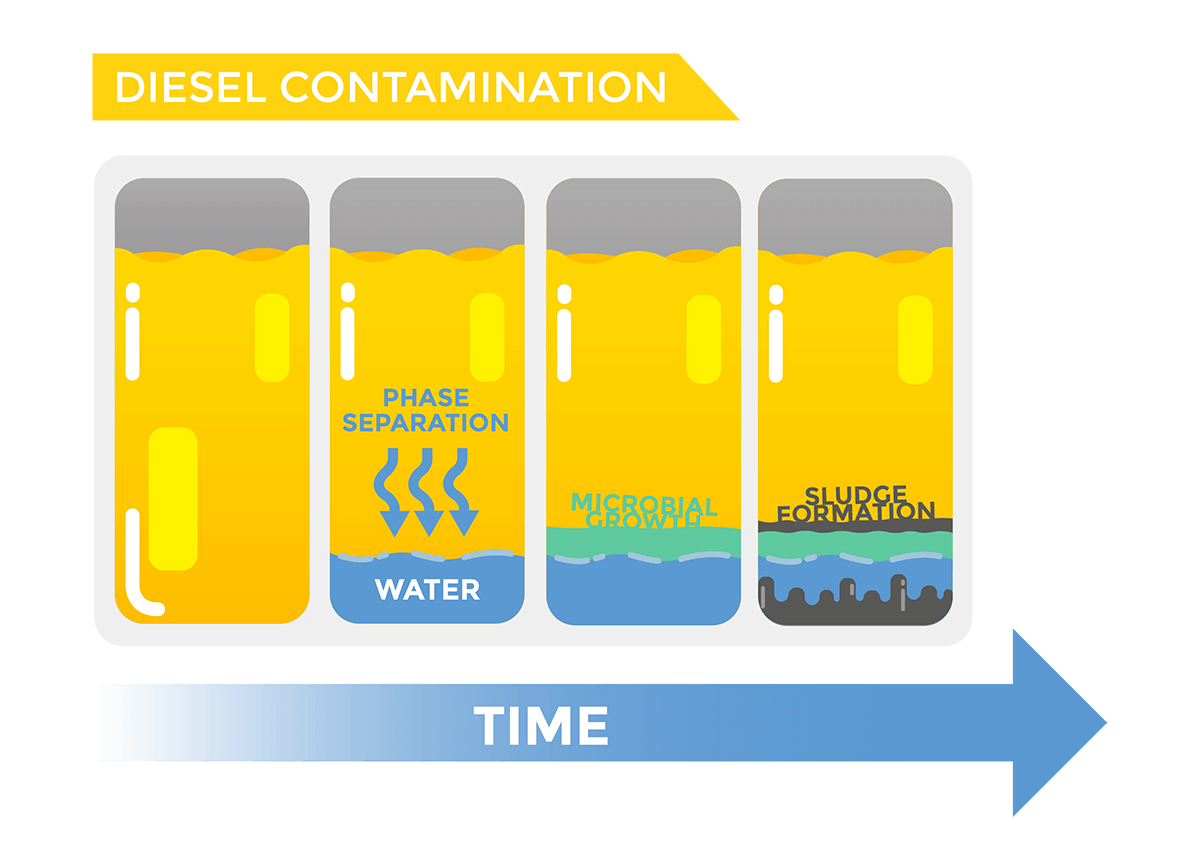
Preventing Corrosion & Unplanned Downtime
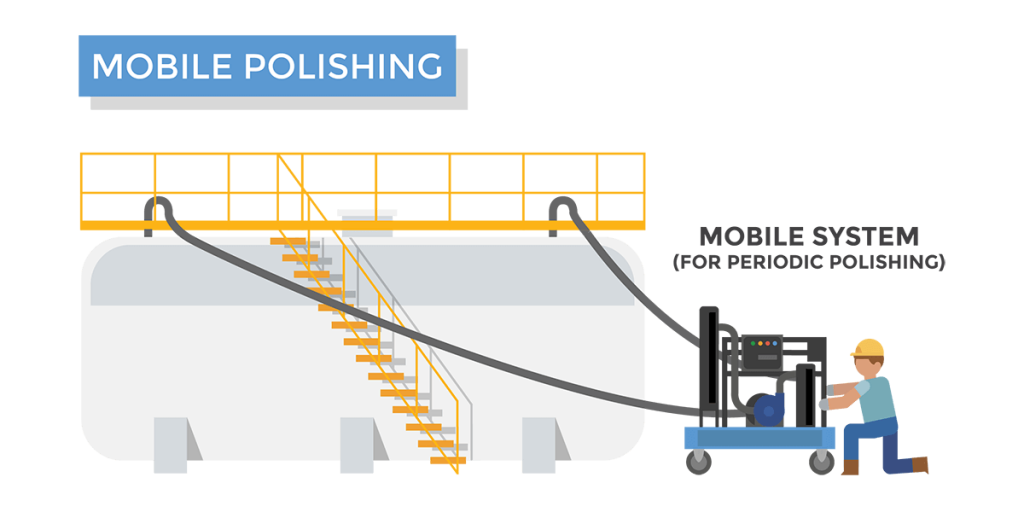
Choice #ane: Periodic Fuel Polishing
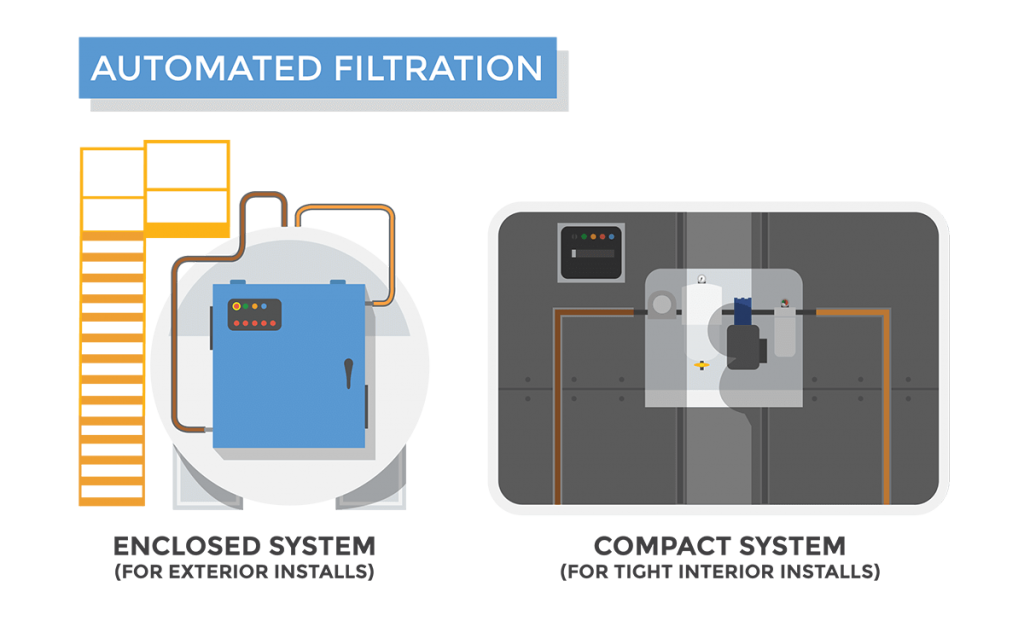
Selection #two: Automated Fuel Filtration
Source: https://axi-international.com/ultra-low-sulfur-diesel-ulsd/
0 Response to "what to use on diesel truck to clean sulfur buildup"
Post a Comment